Temporal Processing and Related Terms

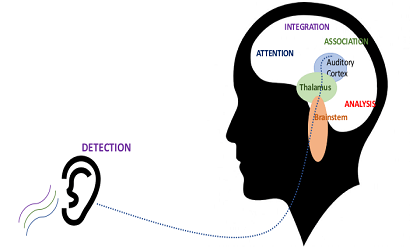
Central Auditory Processing, according to ASHA (2005), “…is the perceptual processing of auditory information in the central auditory nervous system (CANS) and the neurobiological activity that underlies that processing and gives rise to electrophysiologic auditory potentials ” as defined.
Central auditory processing is subdivided into various sub-sections in terms of the mechanism and functions it is responsible for;
• Sound localization and lateralization
• Auditory discrimination
• Auditory pattern recognition
• Temporal processing
• Auditory discrimination in difficult listening conditions
• Auditory discrimination in the presence of distorted acoustic signal
Temporal Processing is the perception of sound or change in sound within a certain temporal field. It is generally examined in four categories;
1-Temporal Sequence: Sequential sounds are processed in order of occurrence. Sequencing of auditory information depends on subject training, type of stimulus, number and duration of stimuli, presentation speed and format. (These are critical variables to consider when developing and performing tests)
2-Temporal Resolution: The perception of rapidly changing signals over time. (To distinguish the shortest gap between two auditory stimuli) This is usually 2-3 ms for short sounds. (Philips, 1999) We call this the ‘temporal resolution threshold’. Temporal auditory acuity has also been defined as minimum integration time. (Green, 1971)
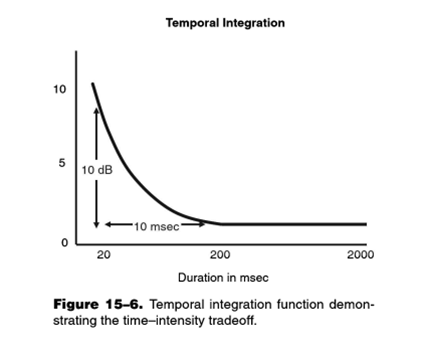
3- Temporal Integration: It is the ability to accumulate and collect the energy of short-term sounds and to add the audio information that comes over time. The duration of stimulation is an important factor affecting temporal attachment.
In the normal hearing population, the threshold increases as the duration increases to approximately 200 ms. (Durrant & Lovrinic, 1995)
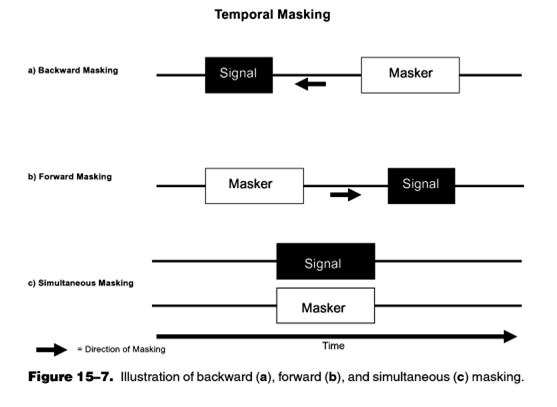
4-Temporal Masking: Temporal masking occurs when a signal and the masker do not overlap temporally. It is the masking of the auditory stimulus by the sound coming before or after it.
The mechanism is not known exactly; temporal masking is thought to be mostly due to the difference in neural firing times of the central hearing system. (Musiek & Chermak, 2013)
Temporal masking depends on the acoustic similarity between mask and signal, masking level and duration and the time between mask and signal.
Masking effect; discrete noise < continuous noise
meaningless speech stimulus < meaningful speech stimulus
In forward masking, masking does not occur if the time interval between the masker and the signal is 200 ms or more.
In backward masking, the mask effect decreases when there is a mask-signal interval between 25 msec and above. (Durant & Lovrinic, 1995)
Temporal processing is very important for temporal organization in relation to daily life. To determine the duration (duration) of voices and the gaps between them; Detecting the prosodic and spectral characteristics of speech for speech and music perception (rhythm, tone, intonation); Understanding in noise (taking advantage of short gaps and focusing on target stimulus); Distinguishing the difference of time between the vocal consonants of variable frequency and intensity formed by laryngeal phonation and the silent consonants of high frequency and low intensity formed by air column shows the importance of temporal processing for temporal organization.
Sometimes only time difference can cause meaning difference. People make sense of the word with this difference in duration.
Remember to share and like. Good luck..